在 VMware ESXi 上安装 Minix
2010年02月11日 | 标签: minix, vmware esxi
VMware ESXi 是业界领先的 hypervisor,更重要的是它现在是免费的,只要在 VMware 上注册一个账号就可以拿到一个免费的 license,下载 iso 后刻盘启动,安装过程非常简单,安装完后界面如下,可以修改的东西不多,可修改管理员密码和网络配置。主要操作和配置需要在一个另外一台机器上(安装 VMware vShpere 客户端)完成。需要注意的是 VMware ESXi 对硬件设备要求很高,好像一般的桌面 PC 都安装不了,VMware ESXi 4.0 Hardware Compatibility List 和这里给出了能运行 VMware ESXi 的兼容硬件设备列表。
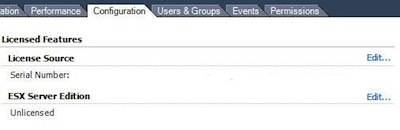
在主控台配置完 ESXi 的网络后在另外一台机器上打开 http://your-ip-address/ 就会看到一个页面,下载和安装 VMware-viclient.exe 客户端工具后就可以用来管理 VMware ESXi. 启动 VMware vShpere Client 后就会发现是个60天试用版本,需要输入 license(虽然是免费的)。VPSee 找了半天才找到输入 license 的地方,不在菜单上,在右边页面的 Configuration tab 下的 Software->Licensed Features:
VMware ESXi 安装成功后就是创建虚拟机、安装 Minix 了,原以为会很顺利,结果昨天因为网卡驱动问题折腾了一上午。安装 Minix 时候会碰到如下问题:
Probing for disks. This may take a short while... AT0-D0: controller not ready AT0-D0: controller not ready AT0-D0: reset failed, driver busy AT0-D1: controller not ready AT0-D1: controller not ready AT0-D1: reset failed, driver busy ...... Found no drivers - can't partition. Autopart tool failed. Trying again.
原因是 VMware ESXi 默认创建的虚拟硬盘设备是 SCSI 的,Minix 不支持 SCSI 只支持 IDE 的,解决办法是 Power Off Minix 虚拟机,在 Edit virtual machine settings 中 Add 一个 Hard Disk 设备并在 Virtual Device Node 中选择 IDE (0:0),然后再启动虚拟机后就可以顺利安装 Minix 了。要注意的是,安装 Minix 一定要安装 Minix 3.1.6 或以上版本,不然就会遇到烦人的网卡驱动问题,昨天花了很长时间才找到问题所在,压根就没有想到会是驱动有 bug,驱动完全不工作也好说,至少可以马上定位问题所在,最怕这种有时候工作有时候不工作的情况,anyway,安完 Minix 后需要配置一下 Minix 环境以便以后操作。
设置静态 IP 地址:
# vi /etc/rc.net ifconfig -l /dev/ip0 -n 255.255.255.0 -h 172.16.20.201 add_route -g 172.16.20.1 daemonize nonamed -L
在系统启动的时候就启动 telnet 和 ftp 服务:
# vi /etc/rc.net intr -d tcpd telnet in.telnetd & intr -d tcpd ftp in.ftpd &
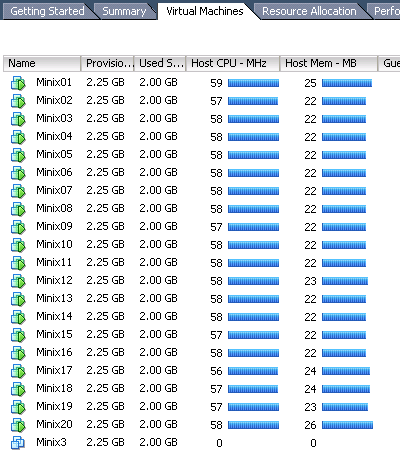
如果要安装很多 Minix 的话,可以在安装和配置好一个 Minix 后导出为一个虚拟机通用模版(VMware ESXi 主菜单上的 File->Export OVF Template… ),然后再利用这个模版(File->Deploy OVF Template… )部署多个 Minix 虚拟机器。下图是刚创建的20个 Minix 虚拟机: